[Java] Mongodb 에서 가장 가까운 위치 데이터 조회하기
서론
시작 부분에서는, 각 개념에 대해 정리를 할 계획이며
Java 에서 Mongodb 데이터의
가장 가까운 위치 데이터를 조회하는 방법이 궁금하신 분은 글 하단에 정리되어 있습니다.
Geo-Spatial Data 란?
지리 공강 데이터를 의미하며, GeoJSON 객체나 lehacy coordinates paris(레거시 좌표 쌍) 로 Geospatial data 를 저장 할 수 있다.
GeoJSON 객체
지구와 같은 구 위에서 geometry 를 계산하기 위해선, 위치 데이터를 GeoJSON 객체 형태로 저장해야 한다.
GeoJSON Data 를 명시하기 위해, 아래와 같은 조건과 함께 embedded document 를 사용해야 한다.
- type 필드엔 GeoJSON object type(Point, Polygon, MultiPoint 등등..) 을 명시한다.
- coordinates 필드엔 객체의 좌표를 명시한다. 만약 위도와 경도 좌표를 지정하는 경우엔 [경도, 위도] 의 순서가 맞다.
- 경도 값 범위는 -180 <= x <= 180 ( 0 : 그리니치 천문대(런던), - : 서쪽, + : 동쪽 )
- 위도 값 범위는 -90 <= y <= 90 ( 0 : 적도, -90 : 남극, +90 : 북극 )
1
<field>: { type: <GeoJSON type> , coordinates: <coordinates> }
예를들어 GeoJSON Point 를 명시하면 아래와 같다.
1
2
3
4
location: {
type: "Point",
coordinates: [-73.856077, 40.848447]
}
MongoDB 에서 지원하는 GeoJSON 객체 목록과 예시는 GeoJSON objects 에서 볼 수 있다.
MongoDB 의 GeoJSON 객체에 대한 geospatial queries 는 구에서 계산된다. MongoDB 의 geospatial queries 는 WGS84 참조 시스템을 사용합니다.
Legacy Coordinate Pairs (레거시 좌표 쌍)
Euclidean plane (유클리드 평면) 상에서 거리를 계산하기 위해선 위치 데이터를 legacy coordinate paris 로 저장하고 2d index 를 사용해야 한다. MongoDB 는 데이터를 GeoJSON Point 타입으로 변환하여 2dsphere index 를 통해 legacy coordinate paris 에서 구면 계산을 지원한다.
데이터를 legacy coordinate paris 로 명시하는 방법에는 배열을 사용하거나 embedded document 를 사용 할 수 있다. (배열 사용을 추천)
배열을 통한 명시 (추천)
1
<field>: [ <x>, <y> ]
만약 위도와 경도 좌표를 명시한다면, 경도를 먼저 쓰고 위도를 그다음에 작성한다.
1
<field>: [<longitude>, <latitude> ]
- 경도 값 범위는 -180 ~ 180
- 위도 값 범위는 -90 ~ 90
embedded document 를 통한 명시
1
<field>: { <field1>: <x>, <field2>: <y> }
만약 위도와 경도 좌표를 명시한다면, 첫번째 필드에는 필드 이름에 상관없이 경도 값을, 두번째 필드에 위도 값을 넣어야 한다.
1
<field>: { <field1>: <longitude>, <field2>: <latitude> }
- 경도 값 범위는 -180 ~ 180
- 위도 값 범위는 -90 ~ 90
legacy coordinate pairs 를 명시하는 두가지 방법중에서, embedded document 를 통한 방법은 몇몇 언어에선 associative map ordering 이 보장되지 않으니 배열을 통한 방법을 추천한다.
Geospatial Indexes (지리공간 인덱스)
MongoDB 는 geospatial queries 를 지원하기 위해 다음과 같은 geospatial index 타입들을 제공한다.
2dsphere
2dsphere index 는 지구와 같은 구에서 geometry 를 계산하는 쿼리들을 지원한다.
2dsphere index 를 생성하기 위해선, db.collection.createIndex() 함수를 사용하고 인덱스 타입에 “2dsphere” 라고 명시해야 한다
1
db.collection.createIndex( { <location field> : "2dsphere" } )
<location field> 는 GeoJSON 객체 혹은 legacy coordinate paris 를 값으로 가질 수 있는 필드이다.
관련된 더 많은 정보는 2dsphere indexes 에서 볼 수 있습니다.
2d
2d index 는 2차원 평면상에서의 geometry 를 계산하는 쿼리를 지원한다. 비록 이 인덱스가 구체 상에서 계산하는 쿼리인 $nearSphere 를 지원 가능하지만, 구와 관련된 쿼리 사용시에는 2dsphere index 를 사용하는게 좋다.
<location field> 는 legacy coordinate paris 를 값으로 갖는 필드입니다.
관련된 더 많은 정보는 2d Indexes 에서 볼 수 있습니다.
1
2
db.컬렉션명.createIndex({ "필드명": "2d" })
db.컬렉션명.createIndex({ "필드명": "2dsphere" })
Mongodb 에서 위 명령어를 사용하면 입력한 컬렉션의 필드명에 지리공간 쿼리를 사용하기 위한 인덱스가 생성된다.
Covered Queries
Geospatial indexes 는 covered query 가 될 수 없습니다. (covered query ? : 쿼리의 조건이나 프로젝션이 인덱스된 필드만 포함해서 다른 document 를 스캔하거나 가져올 필요가 없는 쿼리)
Geospatial Queries (지리공간 쿼리)
NOTE
구체에 대한 쿼리에는 2dsphere index 결과값을 사용하세요.
양극을 감싸는 구형에 대한 쿼리에 2d index 를 사용하는 것은 잘못된 결과값이 나올 수 있습니다.
Geospatial Query Operators (지리공간 쿼리 연산자)
MongoDB 는 아래와 같은 geospatial query 연산자들을 지원한다.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| $geoIntersects | GeoJSON geometry 와 교차하는 geometries 를 선택합니다. 2dsphere index 는 $geoIntersects 를 지원합니다. |
| $geoWithin | GeoJSON geometry 안에 속하는 geometries 를 선택합니다. 2dsphere index 와 2d index 모두 $geoWithin 을 지원합니다. |
| $near | 점과 가까운 순서의 geospatial objects 를 반환합니다. geospatial index 가 필요하며 2dsphere index 와 2d index 모두 $near 를 지원합니다. |
| $nearSphere | 구체에서 점과 가까운 순서의 geospatial objects 를 반환합니다. geospatial index 가 필요하며 2dsphere index 와 2d index 모두 $nearSphere 를 지원합니다. |
더 많은 내용과 예시들은 개별 참조 페이지에서 볼 수 있다. ( $geoIntersects / $geoWithin / $near / $nearSphere )
Geospatial Aggregation Stage
MongoDB 는 아래와 같은 geospatial aggregation pipeline stage 를 지원한다.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| $geoNear | geospatial point 와의 가까움 정도에 의해 정렬된 documents stream 을 반환합니다. geospatial data 에 대한 $match / $sort / $limit 기능을 통합합니다. 반환된 documents 는 추가된 distance 필드가 포함되어있으며 위치 식별자 필드를 포함할 수도 있습니다. $geoNear 은 geospatial index 가 필요합니다. |
더 많은 내용과 예시들은 $geoNear 참조 페이지에서 볼 수 있습니다.
Geospatial Models
MongoDB 의 geospatial query 는 구체 혹은 평평한 표면에서의 geometry 를 해석할 수 있다.
2dsphere index 는 구체에 대한 쿼리 (구체 표면의 geometry 를 해석하는 쿼리) 만 지원한다.
2d index 는 flat 쿼리 (평평한 표면에서의 geometry 를 해석하는 쿼리) 와 몇몇 구체에 대한 쿼리를 지원한다.
2d index 가 몇몇 구체에 대한 쿼리를 지원하긴 하지만, 그렇게 사용한 결과값에는 에러가 있을수 있으니 가능하면 구체에 대한 쿼리에는 2dsphere index 를 사용해야한다.
아래 표는 각 geospatial 연산에서 사용되는 geospatial query 연산자들 (지원되는 쿼리) 을 나열한다.
| Operation | Spherical/Flat Query | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| $near (GeoJSON point, 2dsphere index) | Spherical | GeoJSON 과 2dsphere index 를 함께 사용할 때 | 동일한 기능을 제공하는 $nearSphere 연산자도 보십시오 |
| $near (legacy coordinates, 2d index) | Flat | ||
| $nearSphere (GeoJSON point, 2dsphere index) | Spherical | GeoJSON point 와 2dsphere index 를 사용하는 $near 연산자와 동일한 기능을 제공합니다 | |
| $nearSphere (legacy coordinates, 2d index) | Spherical | 대신 GeoJSON point 를 사용하세요 | |
| $geoWithin: {$geometry: …} | Spherical | ||
| $geoWithin: {$box: …} | Flat | ||
| $geoWithin: {$polygon: …} | Flat | ||
| $geoWithin: {$center: …} | Flat | ||
| $geoWithin: {$centerSphere: …} | Spherical | ||
| $geoIntersects | Spherical | ||
| $geoNear aggregation stage (2dsphere index) | Spherical | ||
| $geoNear aggregation stage (2d index) | Flat |
Example
다음의 documents 를 사용하여 places 라는 이름의 collection 을 생성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
db.places.insert( {
name: "Central Park",
location: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.97, 40.77 ] },
category: "Parks"
} );
db.places.insert( {
name: "Sara D. Roosevelt Park",
location: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.9928, 40.7193 ] },
category: "Parks"
} );
db.places.insert( {
name: "Polo Grounds",
location: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.9375, 40.8303 ] },
category: "Stadiums"
} );
다음 연산은 location 필드에 2dsphere index 를 생성한다.
1
db.places.createIndex( { location: "2dsphere" } )
$near 연산자를 사용한 다음의 쿼리는 명시된 GeoJSON point 로부터 1000 미터 이상 5000 미터 이하의 documents 를 가장 가까운 것부터 가장 먼 순서로 정렬해 반환
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
db.places.find(
{
location:
{ $near:
{
$geometry: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.9667, 40.78 ] },
$minDistance: 1000,
$maxDistance: 5000
}
}
}
)
다음의 geoNear aggregation operation 은 { category: “Parks” } 조건에 맞는 documents 를 명시된 GeoJSON point 로부터 가장 가까운 것부터 가장 먼 순서로 정렬해 반환합니다 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
db.places.aggregate( [
{
$geoNear: {
near: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.9667, 40.78 ] },
spherical: true,
query: { category: "Parks" },
distanceField: "calcDistance"
}
}
] )
Java 환경에서의 적용 방법
인덱스에 사용 될 필드 생성이 되어 있지 않으면서,
컬렉션이 복잡한 경우에는 꼭 인덱스 설정을 미리 하고 필드생성을 해주시길 바랍니다.
location 필드를 생성 후 인덱스 설정을 하니 서버(Springboot)에서 아래와 같이 인덱스를 찾을 수 없다는 예외가 발생했습니다.
1
unable to find index for $geoNear query", "code": 291, "codeName": "NoQueryExecutionPlans"
DB 지리공간 인덱스 설정
Mongodb 컬렉션의 필드에 지리공간 인덱스를 설정하자
컬렉션이 단순한경우에는 아래와 같이 사용 가능합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 둘 중 하나를 사용해야 하고, 2dphere 를 사용하는 걸 추천한다.
db.컬렉션명.createIndex({ "필드명": "2d" })
db.컬렉션명.createIndex({ "필드명": "2dsphere" })
db.NearTest.createIndex({ "location": "2dsphere" })
db.Parents.createIndex({ "child.field3.location": "2dsphere" })
컬렉션이 복잡한 경우에는 아래와 같이 사용해야 합니다.
Mongodb 는 자유도가 몹시 높기 때문에 위경도가 존재하지 않는 데이터가 있다는 가정하에
location 값이 null 인 경우 BE 에서 NPE 익셉션이 발생하기 때문에
위경도가 존재하지 않는다면 해당 필드 자체를 생성하지 말아야 합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Parents : {
"_id" : ObjectId("111111"),
"child" : [
{"field1": "field1"},
{"field2": "field2"},
{
"field3": [
{
"latitude" : 36.111111,
"longitude" : 127.111111
},
{
"latitude" : null,
"longitude" : null
}
]
}
]
}
아래의 경우에 해당된다면 2d 인덱스에 사용 될 필드를 아래와 같이 $cond(조건문) 를 이용해 location 필드를 생성 합니다.
- 위경도 데이터가 따로 존재
- 2d(sphere) index 에 null 이 존재 할 경우
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
db.Parents.aggregate([
{
$set: {
"childs": {
$map: {
input: "$childs",
as: "data",
in: {
"field1" : "$$data.field1",
"field2" : "$$data.field2",
"field3": {
$cond: {
if: { $eq: [{ $size: "$$data.field3" }, 0] },
then: [],
else: {
$map: {
input: "$$data.field3",
as: "coord",
in: {
$cond: {
if: {
$and: [
{ $ne: [ "$$coord.latitude", null ] },
{ $ne: [ "$$coord.longitude", null ] }
]
},
then: {
"location": {
x: "$$coord.longitude",
y: "$$coord.latitude"
},
"timestamp": "$$coord.timestamp"
},
else: null
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
{
$out: "Parents"
}
])
Entity(Document) 지리공간 인덱스 설정
엔티티(도큐먼트)에서 Legacy Coordinate Pairs (레거시 좌표 쌍) 의 값을 가진 필드에
@GeoSpatialIndexed(type = GeoSpatialIndexType.GEO_2DSPHERE) 를
추가해 해당 값이 지리공간 인덱스라는걸 알려주자
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.GeoSpatialIndexType;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.GeoSpatialIndexed;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Field;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.MongoId;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@Entity
@Document(collection = "NearTest")
public class NearTestEntity {
@MongoId
@Column(name="_id")
@Field(name="_id")
private String _id;
@Column(name="timestamp")
@Field(name="timestamp")
private Long timestamp;
@Column(name="location")
@Field(name="location")
@GeoSpatialIndexed(type = GeoSpatialIndexType.GEO_2DSPHERE)
private Point location;
@Builder
public NearTestEntity(String _id, Long timestamp,Point location
) {
this._id = _id;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.location = location;
}
}
DB 데이터 저장
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
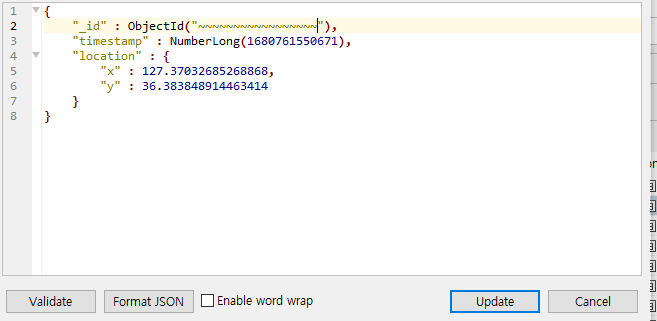
{
"_id" : ObjectId("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~"),
"timestamp" : NumberLong(1680761550671),
"location" : {
"x" : 127.37032685268868,
"y" : 36.383848914463414
}
}
Repository 함수 추가
Repository 규칙에 맞게 함수명을 작성해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Distance;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import org.springframework.data.querydsl.QuerydslPredicateExecutor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import open.platform.model.entity.NearTestEntity;
@Repository
public interface NearTestRepository extends MongoRepository<NearTestEntity, String>, QuerydslPredicateExecutor<NearTestEntity> {
List<NearTestEntity> findByLocationNear(Point point, Distance distance);
NearTestEntity findTopByLocationNear(Point point, Distance distance);
}
데이터 조회
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
import org.springframework.data.geo.Distance;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Metrics;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
Point point = new Point(127.37066163281584, 36.38321571451524);
Distance distance = new Distance(100.0, Metrics.KILOMETERS);
List<NearTestEntity> entities = nearTestRepository.findByLocationNear(point, distance);
NearTestEntity entity = nearTestRepository.findTopByLocationNear(point, distance);

Leave a comment